Web Content Display Web Content Display
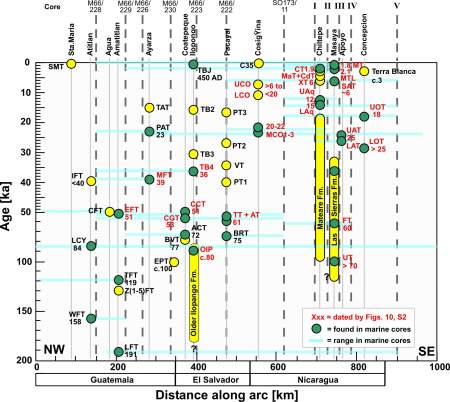
TephrostratigraphyAssessing the volatile output from evolving magma systems in explosive eruptions required to constrain the temporal succession and magnitudes of widespread tephras along the Central American Volcanic Arc (CAVA) in addition to petrological/geochemical analyses of bulk rocks, minerals, and matrix and inclusion glasses. Only some neighbouring volcanic complexes have interfingering stratigraphic tephra succession onshore. Combining work on land and marine sediment cores, we have established the tephrostratigraphic framework of the past >200 ka along the CAVA and newly build up or revised older tephra successions and sampled every recognized tephra (71) along the arc. We also obtained new time constraints for 11 unknown ages of tephras by using pelagic sedimentation rates. Altogether this forms the basis of all other results obtained in this project. The tephra succession shows that widespread tephras account for >65% of the entire extrusive magma production of the CAVA and that such production evolved in cycles with periods of order 105 years.
Figure 3: Composite tephrostratigraphy of Central America showing the position along the arc versus age of tephras. Green dots mark tephras correlated with the marine record. Red labels show tephras newly dated. Blue lines show along-arc spread of ash layers on the Pacific seafloor. Gray bold-dashed lines indicate projected core positions, Roman numerals represent groups of closely adjacent. |
 Events Events
Kieler Wissenschaftler fühlen den 'Puls der Erde' Wie funktioniert die Recyclingmaschine der Erde?Nach elf Jahren endet der Kieler Sonderforschungsbereich 574 zu Subduktionszonen Final colloquium of SFB 574 Teilprojekt ÖffentlichkeitsarbeitMEERESFORSCHUNG FÜR MICH UND DICH |
|
©SFB574 // Wischhofstrasse 1-3 // D-24148 Kiel // T. +49 (0)431 600 1413 // elange [AT] geomar.de